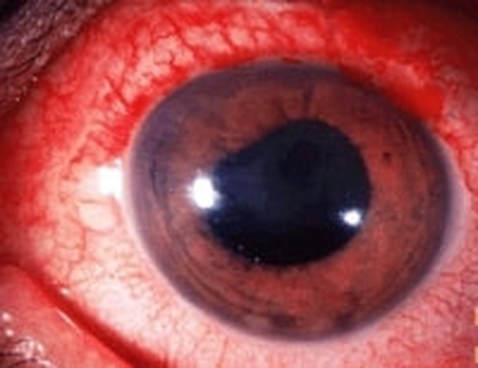
Uveitis...Red Eyes & Eye Pain
Symptoms of Spondylosis:
The types and severity of symptoms of spondylosis vary between individuals and will differ depending on the specific type of spondylosis. Cervical spondylosis affects the cervical spine of the neck. Thoracic spondylosis affects the thoracic spine of the mid and upper back, and lumbar spondylosis affects the lumbar spine of the lower back.
At the onset of the condition, which can begin by age 30, many people do not have symptoms. Symptoms of spondylosis can be vague and develop slowly, or in some cases they may occur suddenly. Symptoms often do not appear until the middle years or later. Some people never develop symptoms.
Symptoms of lumbar spondylosis include lower back pain, commonly beginning at age 40 or later. There can also be lower back stiffness in the morning. Lower back pain can occur with movement and activity or while sitting still. Standing or lying down tends to be less painful than sitting for long periods of time. Lifting and bending often aggravates lower back pain due to lumbar spondylosis.
Symptoms of thoracic spondylosis can include mid-back pain during hyperextension or flexion of the back.
Symptoms of cervical spondylosis include neck pain. Neck pain can progress in severity over time and can lead to neck stiffness and difficulty moving the neck. Pain may radiate to the arms or shoulders. People with spondylosis may also have muscle weakness and numbness and tingling of the shoulder, arms, hands or legs. Headaches, dizziness, and loss of balance may also occur. A herniated disc or bulging disc are also possible symptoms.
In some cases, complications are possible. If the nerves that control the bladder or anal sphincter are compressed, a person may have difficulty controlling the bladder or anal sphincter and experience urinary incontinence or fecal incontinence. In rare cases cervical radiculopathy and cervical myelopathy can occur and lead to permanent disability.
Other possible complications of spondylosis include spinal osteoarthritis, chronic pain, and disability....more about Spondylosis »
Symptoms of Spondylosis
The list of signs and symptoms mentioned in various sources for Spondylosis includes the 12 symptoms listed below:
Complications list for Ankylosing Spondylitis:
Complications and sequelae of Ankylosing Spondylitis from the Diseases Database include:
Uveitis: Introduction
·Uveitis: Symptoms
Uveitis: Treatments
Uveitis: Misdiagnosis
Symptoms of Uveitis
Symptoms of Uveitis: IntroductionSymptoms of uveitis can affect one or both eyes. Symptoms are due to inflammation, swelling and irritation of the affected eye or eyes. Symptoms include eye pain, eye redness, and blurred vision. There also may be a general discomfort in the affected eye and a sensitivity to light (photosensitivity).
If not diagnosed and treated promptly, complications of uveitis can be serious. Complications can include cataracts, glaucoma, and blindness. Symptoms of these complications can be similar to symptoms of uveitis.
Symptoms of uveitis can recur even with treatment....more about Uveitis »
Symptoms of UveitisThe list of signs and symptoms mentioned in various sources for Uveitis includes the 9 symptoms listed below:
Complications list for Uveitis:
The list of complications that have been mentioned in various sources for Uveitis includes:
Complications and sequelae of Uveitis from the Diseases Database include:
Treatments for Uveitis:
Treatment of uveitis includes corticosteroid eye drops or ointment. A corticosteroid medication reduces inflammation and pain of the eye and helps to improve symptoms. Treatment can also lessen the risk of developing complications, such as glaucoma and cataracts. In some cases a corticosteroid medication may be given by injection or in pill form.
Eye drops that enlarge (dilate) the pupil may also be prescribed to minimize the development of complications.
Uveitis can recur after treatment, and it can result in the development of serious complications, such as cataracts, glaucoma, and blindness. Because of this it is important to seek regular follow-up eye care during and after an episode of uveitis to re-evaluate and monitor the eyes.
Treatment List for Uveitis - Conventional Treatments
The list of treatments mentioned in various sources for Uveitis includes the following list. Always seek professional medical advice about any treatment or change in treatment plans.
Alternative Treatments for Uveitis
Alternative treatments or home remedies that have been listed as possibly helpful for Uveitis may include:
The types and severity of symptoms of spondylosis vary between individuals and will differ depending on the specific type of spondylosis. Cervical spondylosis affects the cervical spine of the neck. Thoracic spondylosis affects the thoracic spine of the mid and upper back, and lumbar spondylosis affects the lumbar spine of the lower back.
At the onset of the condition, which can begin by age 30, many people do not have symptoms. Symptoms of spondylosis can be vague and develop slowly, or in some cases they may occur suddenly. Symptoms often do not appear until the middle years or later. Some people never develop symptoms.
Symptoms of lumbar spondylosis include lower back pain, commonly beginning at age 40 or later. There can also be lower back stiffness in the morning. Lower back pain can occur with movement and activity or while sitting still. Standing or lying down tends to be less painful than sitting for long periods of time. Lifting and bending often aggravates lower back pain due to lumbar spondylosis.
Symptoms of thoracic spondylosis can include mid-back pain during hyperextension or flexion of the back.
Symptoms of cervical spondylosis include neck pain. Neck pain can progress in severity over time and can lead to neck stiffness and difficulty moving the neck. Pain may radiate to the arms or shoulders. People with spondylosis may also have muscle weakness and numbness and tingling of the shoulder, arms, hands or legs. Headaches, dizziness, and loss of balance may also occur. A herniated disc or bulging disc are also possible symptoms.
In some cases, complications are possible. If the nerves that control the bladder or anal sphincter are compressed, a person may have difficulty controlling the bladder or anal sphincter and experience urinary incontinence or fecal incontinence. In rare cases cervical radiculopathy and cervical myelopathy can occur and lead to permanent disability.
Other possible complications of spondylosis include spinal osteoarthritis, chronic pain, and disability....more about Spondylosis »
Symptoms of Spondylosis
The list of signs and symptoms mentioned in various sources for Spondylosis includes the 12 symptoms listed below:
- Neck pain
- Pain spreading from neck down arms
- Lumbar pain
- Lower back pain
- Leg pain
- Arm pain
- Stiff neck
- Stiff lumbar region
- Muscle weakness
- Arm weakness
- Movement difficulty
- Muscle spasms around the spine
- more information...»
Complications list for Ankylosing Spondylitis:
Complications and sequelae of Ankylosing Spondylitis from the Diseases Database include:
- Cauda equina syndrome
- Mitral valve incompetence
- ESR raised
- Atrioventricular node conduction block
- Mitral valve stenosis
- Chest pain
- Enthesopathy
- Spondylitis
- Uveitis
Uveitis: Introduction
- Uveitis is a rare condition in which there is inflammation of the middle layer of the eye called the uvea. A healthy uvea is vital to maintaining a normal blood supply to the retina of the eye. The retina is a light-sensitive membrane that lines the back of the eyes and transmits converts light into electrical impulses and transmits them to the optic nerve and the brain.
- The cause of uveitis is often unknown, but can in some cases uveitis can be due to an infection of the herpes simplex virus or herpes zoster virus. Uveitis can also result from an autoimmune disorder. In an autoimmune disorder, the body's immune system mistakes the tissues of the eye as foreign and potentially dangerous to the body and attacks them.
- Symptoms of uveitis include eye pain, or discomfort, eye redness, blurred vision, and sensitivity to light (photophobia). Uveitis can affect one or both eyes. Complications of uveitis can be serious and permanently affect vision. To learn more about other important symptoms and complications, refer to symptoms of uveitis.
- Uveitis can happen to anyone, but most often occurs to young adults.
- Diagnosing uveitis begins with taking a thorough personal and family medical history, including symptoms, and completing a physical examination that includes a thorough eye examination. This will rule out eye conditions and diseases with similar symptoms.
- An eye examination includes testing pupil response to light, visual acuity or sharpness of vision, checking the sharpness of peripheral vision, and testing the pressure of the inside the eye. The outer eye is examined using an instrument called a slit lamp, and the inner eye is examined using an instrument call an ophthalmoscope. Another test involves temporarily staining the eye with a special eye drop that makes a corneal abrasion, which can mimic uveitis, visible to the clinician.
- A diagnosis of uveitis may be missed or delayed because symptoms can be similar to symptoms of other disorders, diseases or conditions. To learn more about disorder, diseases and conditions that can mimic uveitis, refer to misdiagnosis of uveitis.
- Treatment for uveitis includes medications and regular eye care to monitor the disorder. For more details on treatment plans, refer to treatment of uveitis. ...more »
- Uveitis: Inflammation of the inner eye, which includes the iris, the ciliary body that holds the lens of the eye; and the choroid plexus, a ... more about Uveitis.
- Uveitis: A condition which is characterised by the inflammation of the uvea of the eye. More detailed information about the symptoms, causes, and treatments of Uveitis is available below.
·Uveitis: Symptoms
- Symptoms of uveitis can affect one or both eyes. Symptoms are due to inflammation, swelling and irritation of the affected eye or eyes. Symptoms include eye pain, eye redness, and blurred vision. There also may be a general discomfort in the affected eye and a sensitivity to light (photosensitivity).
- If not diagnosed and treated promptly, complications of uveitis ...more symptoms »
Uveitis: Treatments
- Treatment of uveitis includes corticosteroid eye drops or ointment. A corticosteroid medication reduces inflammation and pain of the eye and helps to improve symptoms. Treatment can also lessen the risk of developing complications, such as glaucoma and cataracts. In some cases a corticosteroid medication may be given by injection or in pill form.
- Eye ...more treatments »
Uveitis: Misdiagnosis
- A diagnosis of uveitis may be delayed or missed because symptoms of uveitis can be similar to symptoms of other diseases and conditions, such as watering eye, subconjunctival hemorrhage, scleritis, cataracts, glaucoma, choroiditis, dry eye, blepharitis, andcorneal ulcer. ...more misdiagnosis »
Symptoms of Uveitis
Symptoms of Uveitis: IntroductionSymptoms of uveitis can affect one or both eyes. Symptoms are due to inflammation, swelling and irritation of the affected eye or eyes. Symptoms include eye pain, eye redness, and blurred vision. There also may be a general discomfort in the affected eye and a sensitivity to light (photosensitivity).
If not diagnosed and treated promptly, complications of uveitis can be serious. Complications can include cataracts, glaucoma, and blindness. Symptoms of these complications can be similar to symptoms of uveitis.
Symptoms of uveitis can recur even with treatment....more about Uveitis »
Symptoms of UveitisThe list of signs and symptoms mentioned in various sources for Uveitis includes the 9 symptoms listed below:
- Hazy vision
- Vision disturbance
- Floaters
- Pruritus
- Decreased visual acuity
- Discharge
- Deep eye pain
- Conjunctival vessel dilation
- Photophobia
- more information...»
Complications list for Uveitis:
The list of complications that have been mentioned in various sources for Uveitis includes:
Complications and sequelae of Uveitis from the Diseases Database include:
- Eye pain
- Iris abnormality
- Cataracts
- Heterochromic iris
- Anisocoria
- Hyperlacrimation
- Pupillary constriction
- Glaucoma, secondary
- Photophobia
Treatments for Uveitis:
Treatment of uveitis includes corticosteroid eye drops or ointment. A corticosteroid medication reduces inflammation and pain of the eye and helps to improve symptoms. Treatment can also lessen the risk of developing complications, such as glaucoma and cataracts. In some cases a corticosteroid medication may be given by injection or in pill form.
Eye drops that enlarge (dilate) the pupil may also be prescribed to minimize the development of complications.
Uveitis can recur after treatment, and it can result in the development of serious complications, such as cataracts, glaucoma, and blindness. Because of this it is important to seek regular follow-up eye care during and after an episode of uveitis to re-evaluate and monitor the eyes.
Treatment List for Uveitis - Conventional Treatments
The list of treatments mentioned in various sources for Uveitis includes the following list. Always seek professional medical advice about any treatment or change in treatment plans.
- Corticosteroid eyedrops
- Oral corticosteroids
- Treatment of any underlying cause
- Glucocorticoids steroids
- Topical eye drops
- Prednisolone acetate
- Oral prednisolone
- Topical cytoplegics
- Atropine
- Homatropine
- Antimetabolite medication
- Methotrexate
Alternative Treatments for Uveitis
Alternative treatments or home remedies that have been listed as possibly helpful for Uveitis may include:
- Salba seeds and salba seed oil
- more treatments »
Sterile MSM Eye Drops with Vitamin C
|
NATURAL EYE CARE: I use Liquid MSM with Vitamin C as my Natural Eye drop for Uveitis. I have a philosophy that whatever goes on my skin should be able to go in my mouth. This eye drop goes in my eyes and in my mouth.
This product is sterile and non-toxic, and thus safe to apply directly to the eyes. Using Liquid MSM as eye drops is any easy, safe way to assist in removing eye dryness, eye redness, eye pain and eye inflammation, also unwanted residue, and to help maintain the cleanliness of the eyes. MY Ophthalmologist advised using it 4 times per day. So, I use two drops x 4, every day. Works much better than the steroid eye drops that were initially prescribed for me. SAFE, NATURAL, AND NON-TOXIC: Liquid MSM with Vitamin C is safe, sterile, and non-toxic. Thousands have safely and effectively used this product, both for internal consumption and applied directly to the eyes HIGH QUALITY AND ORGANIC INGREDIENTS: The MSM in this product is derived from an all-natural, organic compound. This product also contains high quality Vitamin C, in the form of Calcium Ascorbate, which studies have shown is the most efficient form of Vitamin C on the market. Lastly, the base liquid is distilled water mixed with Homeopathic Cell Salt Blend. |
Safety Information
While this product is known to be completely safe for both internal consumption and application directly to the eyes, as with all such products, use as directed by your health care professional.
Indications
Floaters, Eye Problems, Damaged Vessels in Eyes, dry eyes, eye inflammation.
Ingredients
Distilled Water, Organic MSM (methylsulfonylmethane), and Naturally-Derived Vitamin C (Calcium Ascorbate), Homeopathic Cell Salt Blend.
Directions
For internal consumption, add 1 to 5 drops in 8 ounces of your favorite beverage once per day, or as directed by your healthcare professional. For eyes, use 1 to 3 drops in each eye, 1 to 3 times per day, or as directed by your health care professional. For eye drops, it's best to start with less drops, and work up slowly. My Ophthalmologist advised that i used 1-2 drops 4x/day. Yep, I told him I wasn't using the steroids, I am using this natural product that has no side effects for me.
Legal Disclaimer
These statements have not been evaluated by the FDA. Consult with your healthcare professional before use.
Safety Information
While this product is known to be completely safe for both internal consumption and application directly to the eyes, as with all such products, use as directed by your health care professional.
Indications
Floaters, Eye Problems, Damaged Vessels in Eyes, dry eyes, eye inflammation.
Ingredients
Distilled Water, Organic MSM (methylsulfonylmethane), and Naturally-Derived Vitamin C (Calcium Ascorbate), Homeopathic Cell Salt Blend.
Directions
For internal consumption, add 1 to 5 drops in 8 ounces of your favorite beverage once per day, or as directed by your healthcare professional. For eyes, use 1 to 3 drops in each eye, 1 to 3 times per day, or as directed by your health care professional. For eye drops, it's best to start with less drops, and work up slowly. My Ophthalmologist advised that i used 1-2 drops 4x/day. Yep, I told him I wasn't using the steroids, I am using this natural product that has no side effects for me.
Legal Disclaimer
These statements have not been evaluated by the FDA. Consult with your healthcare professional before use.
|
Uveitis: Is the Diagnosis Correct? The first step in getting correct treatment is to get a correct diagnosis. Differential diagnosis list for Uveitis may include: |
Complications of Ankylosing Spondylitis are secondary conditions, symptoms, or other disorders that are caused by Ankylosing Spondylitis. In many cases the distinction between symptoms of Ankylosing Spondylitis and complications of Ankylosing Spondylitis is unclear or arbitrary.